Lua Scripts - GTA 5 Mod Menu (Samurai’s Script) – A Clean-Sheet Lua Scripting System for Extending Gameplay in Grand Theft Auto V
Samurai's Scripts is a structured, Lua-based scripting system for extending and streamlining user interactions in the game Grand Theft Auto V (GTA V) by utilizing current mod-menu platforms. Unlike most simple toggle-feature Lua scripts, Samurai's Scripts functions as a foundational scripting system, managing how commands are executed, backend handlers are managed, weapon groups are categorized, keybinds are implemented, and the entire system is initialized cleanly and efficiently. The samurais_scripts.lua file that was uploaded represents the initial entry-point and bootstrapping layer of the overall script ecosystem. While it doesn't implement direct gameplay functionality, its primary objective is to create a runtime environment, define commands, manage weapon data, and to ensure that every other system that depends upon them is completely initialized before user interactions begin. Samurai's Scripts' architecture is pivotal to its ability to remain stable, scalable, and maintainable for the long-term.
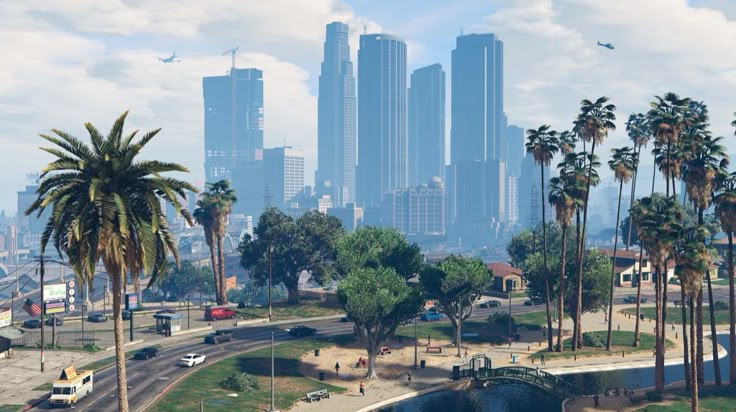
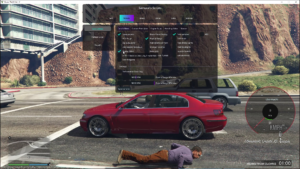
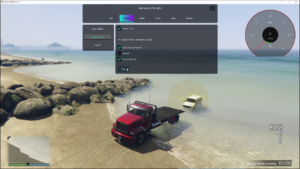
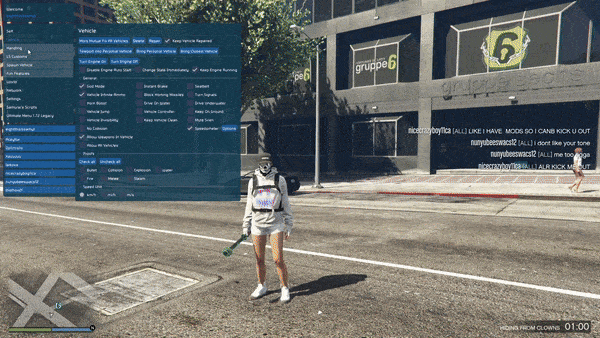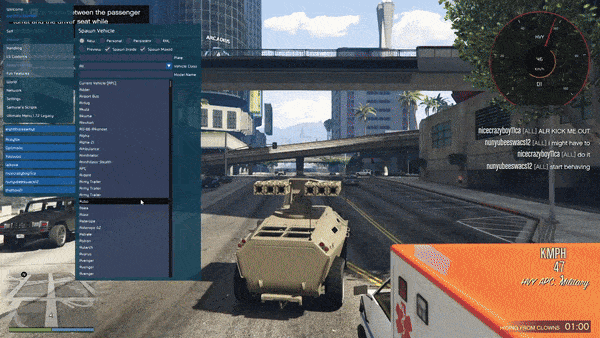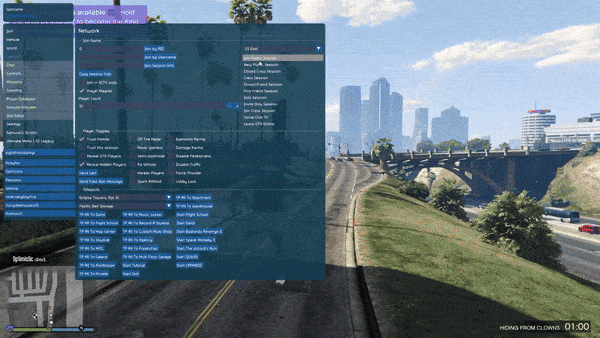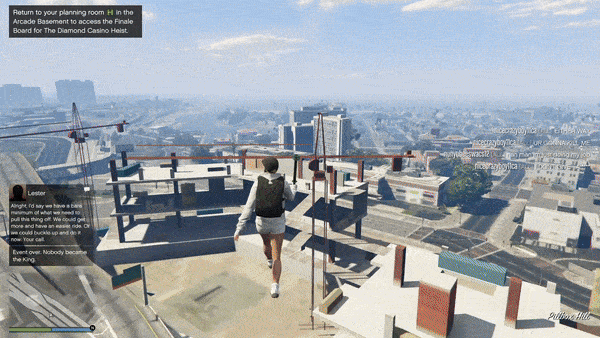
In-Game Screenshots :
Video of the Script
Credits to Dev - #L7NEG Sharing the Script
Download Links:
Initialization of Dependencies and Script Initiation
As soon as the script is initiated, it disables any warning messages regarding diagnostics and lowercase globals to represent the controlled and organized usage of globally accessible objects within the framework. As opposed to allowing uncontrolled and chaotic global object pollution, Samurai's Scripts uses predefined and internally managed global systems that are initialized in a predetermined order. Following the disabling of diagnostics and global object warnings, the script initializes and loads any necessary modules, including a central command registry and an initialization file. These imported modules are the backbone of the framework; they ensure that all the fundamental libraries, utilities, and system components are loaded prior to executing the script. By isolating the definition of commands from the logic that executes those commands, the script maintains a clean division of responsibility. Following the importation of modules, the script initializes its core sub-systems:
- Systems for managing pointers
- Queues for serialization
- Handlers for backend communication
- Modules for translation and localizing
- Components for graphical interfaces
By initializing the various sub-systems in stages, Samurai's Scripts guarantees that no system attempts to execute prior to having all necessary dependencies being initialized. Premature access to uninitialized systems is one of the leading causes of crashes and undefined behavior in complex GTA V scripting systems. Samurai's Scripts eliminates these potential problems by establishing a predetermined order for initializing all of the sub-systems.
Execution Model Using Fibers to Support Non-Blocking Performance
Another pivotal design decision made in Samurai's Scripts is the utilization of an execution model using fibers. Instead of initiating the execution of the initialization logic on the main thread of the game, the script executes within a managed fiber. The managed fiber allows long-running operations (e.g., registering commands, performing pattern scanning) to occur without causing the game or mod-menu interface to freeze. Within the managed fiber, the script utilizes the os.clock() function to record a start time. The start time is subsequently utilized to determine the total load time of the script, providing a basis for debugging and performance analysis. Although measuring load duration may appear to be a relatively trivial matter, it demonstrates a developer who focuses on optimizing and providing transparency. The managed fiber also permits the script to yield control graciously while waiting for external processes (e.g., memory pattern scanning) to complete. This approach significantly reduces the likelihood of experiencing frame drops during the initialization of the script.
Registration of Centralized Command Registry
One of the principal responsibilities of this script is command registration. Commands are retrieved from a centralized registry. Each command is defined with a callback function and any number of optional parameters. The script iterates through the centralized registry and registers each command with the command executor. The benefits of this design include:
- Modularity - Commands can be added/removed/modified at will without affecting the core loader.
- Consistency - All commands are registered in the same way, regardless of implementation.
- Scalability - Adding new features can add new commands without altering existing logic.
After registering the primary commands, the script invokes a secondary command registration layer specifically for menu-related actions. This implies that the script is integrated with a larger mod-menu ecosystem where user-exposed actions are logically grouped and presented through a standardized interface instead of being scattered through arbitrary callbacks. The multi-layered command-execution system is particularly beneficial for larger scripts because it prevents the command-execution logic from becoming entangled and difficult to maintain.
Organization and Data Structure of Weapons
A substantial portion of the script is dedicated to organizing and structuring weapons. Rather than statically defining a weapon list, Samurai's Scripts dynamically queries for weapons that belong to a particular group type. Each category (i.e., melee weapons, handguns, assault rifles, shotguns, SMGs, machine guns, sniper rifles, heavy weapons, and throwables) is queried individually. This approach to dynamically querying for weapons ensures that the script is compatible with any future changes that Rockstar may make to weapons within a group, and therefore minimizes the need for manual maintenance. In addition to the standard categories, the script also organizes miscellaneous weapon types (i.e., petrol cans, stun guns, and tranquilizers). These weapon types are collected separately and then combined into a single, unified list of weapons. This approach to collecting weapon types demonstrates intentional grouping, which enables downstream features to selectively target specific groups of weapon types without creating redundant logic. Finally, the script combines all of the major weapon categories into a single, unified list of weapons. This unified list is likely to be utilized by downstream features that require a unified view of all of the weapon types in the game, such as weapon management menus, weapon selection systems, and automatic gameplay mechanics.
Keybind Registration and Vehicle Interactions
The script registers multiple keybinds utilizing numeric keypad inputs. Each of the registered keybinds corresponds to a vehicle interaction method, permitting the player to initiate a directional ram action when inside a vehicle. These keybinds exemplify a clean input-handling methodology:
- Each keybind is registered to a unique callback function.
- Vehicle interaction is abstracted to a self-referential method.
- Actions are contextual - they only operate when a vehicle exists.
This level of abstraction creates a clean and predictable keybind logic that is easy to read and safe. The script does not directly manipulate the vehicle entity; instead, the script passes the request for behavior to a well-defined method of the vehicle entity. This prevents the possibility of referencing a null or invalid vehicle entity, which are two of the leading causes of runtime errors in GTA V scripts.
Synchronization of Pattern Scanning
Prior to completing the initialization of the script, the script waits for the completion of the pattern scanning operation. Pattern scanning is a critical operation that is necessary to dynamically locate memory addresses that correspond to the version of the game in which the script is currently operating. Instead of assuming that the pattern scanning operation will immediately complete, the script continuously yields control until the pattern scanning operation has completed. This synchronization of the pattern scanning operation prevents any dependent systems from attempting to reference memory addresses that are either incomplete or invalid. Additionally, this example of synchronized pattern scanning is representative of Samurai's Scripts defensive programming approach - prioritizing safety over efficiency. Only after the script confirms that the pattern scanning operation has been completed will the script proceed to perform the final logging operations.
Logging of Backend Debugging Information and Reporting of Load Time
Following the successful completion of all of the initialization tasks, the script logs a debugging message that reports the total load time of the script in milliseconds. This message is transmitted through the backend debugging system, as opposed to being printed directly to the screen. There are numerous benefits of transmitting the debugging message through the backend debugging system, including:
- Centralized log management
- Configurable verbosity levels
- Easier debugging across multiple environments
Reporting of load time also provides valuable information to both developers and advanced users. If the startup time of the script increases after a new feature has been added, this metric can be used to identify performance regressions early.
Strengths and Design Intent of Architectural Decisions
The overall design of samurais_scripts.lua demonstrates a framework-first mindset. Rather than focusing on immediate gameplay effects, the script prioritizes:
- Clean initialization flow
- Modular command management
- Dynamic data retrieval
- Non-blocking execution
- Defensive synchronization
While many smaller community scripts neglect these concepts, they are essential to maintaining a long-term project that evolves across multiple versions. The script's reliance on structured systems (e.g., registries, managers, handlers) implies that it is part of a larger ecosystem, rather than a standalone mod. Therefore, the script is well-positioned for continuing expansion and collaboration.
Performance and Stability Considerations
From a performance perspective, Samurai's Scripts limits heavy processing activities to the initialization phase. Heavy processing activities are restricted to the initialization phase and occur within the managed fiber. The runtime logic of the script is lightweight and reliant upon pre-constructed data structures and registered callbacks.